Understanding Hyperpigmentation at a Cellular Level

Article Written By Research Contributor, Medically Reviewed By Experts Of Serena Medical Center
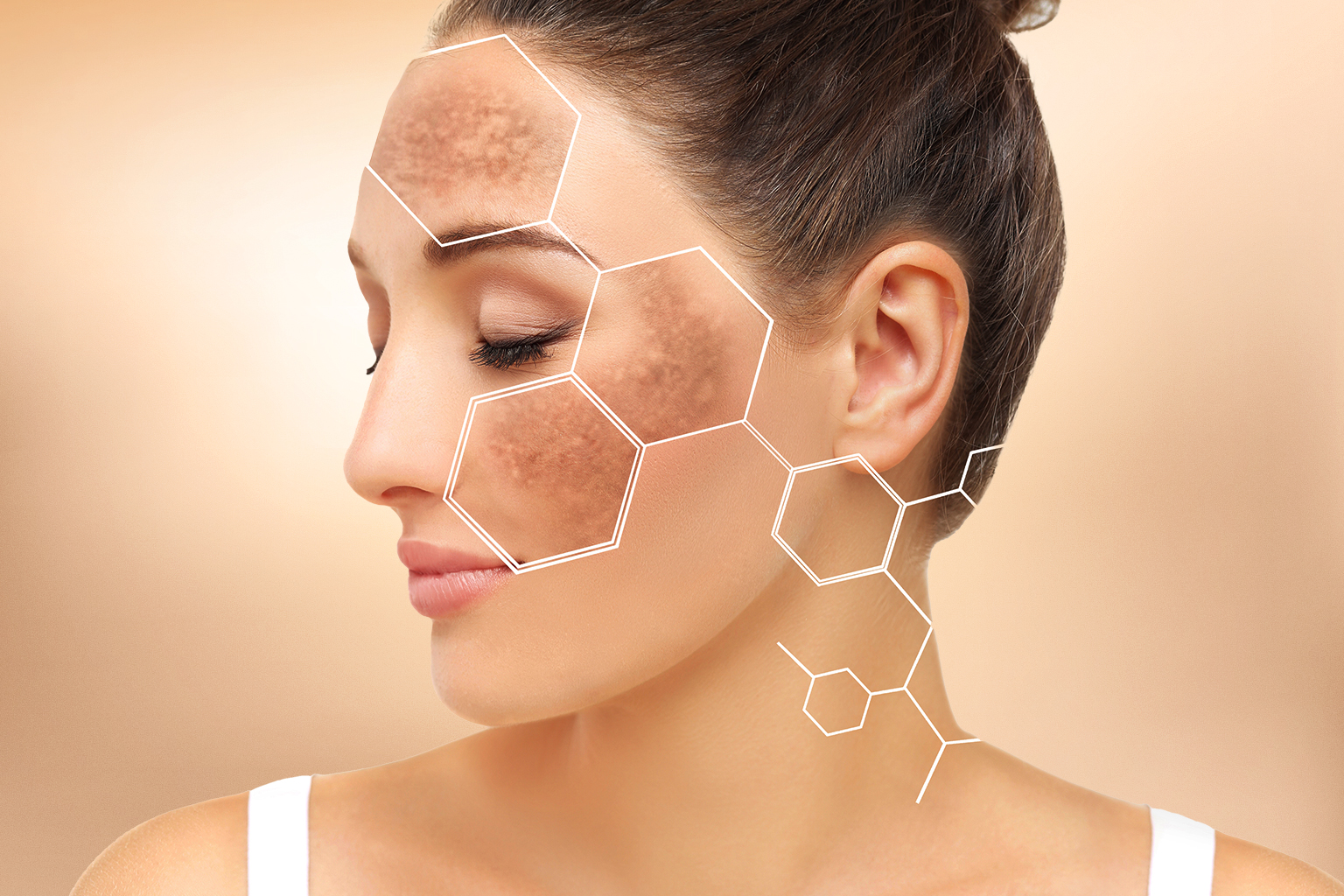
So, what is hyperpigmentation exactly? It refers to patches of skin that appear darker than the surrounding areas due to excess melanin production or uneven melanin distribution. To understand what is hyperpigmentation, it is necessary to first look at normal skin physiology. Melanocytes produce melanin through enzymatic activity regulated by tyrosinase. This pigment is transferred to keratinocytes, defining natural skin tone and protecting against ultraviolet radiation. In clinical terms, what is hyperpigmentation is a disruption of this regulated process.
Problems arise when melanocyte activity increases abnormally or melanin disperses irregularly across skin layers. Pigmentation may remain confined to the epidermis or extend into the dermis, with each depth influencing treatment response. Epidermal involvement typically responds better to topical care, while dermal pigmentation often requires procedural intervention. Accurate depth assessment using Wood’s lamp and dermoscopy establishes diagnosis and guides hyperpigmentation treatment planning.
What Causes Hyperpigmentation: Clinical Triggers and Risk Factors
Understanding what causes hyperpigmentation requires evaluating multiple contributing factors rather than a single trigger. Ultraviolet exposure remains the primary cause, stimulating melanocytes through inflammatory and oxidative pathways. Hormonal fluctuations involving estrogen and progesterone also play a significant role, particularly in melasma associated with pregnancy and oral contraceptives. Clinically, what causes hyperpigmentation often reflects cumulative biological stress on melanocyte regulation.
Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation is another frequent diagnosis, following acne, burns, cosmetic procedures, or allergic reactions. Inflammation stimulates excess melanin as part of tissue repair. Genetic predisposition, medication use, and systemic conditions further complicate the picture. Identifying what causes hyperpigmentation is essential, as unmanaged triggers reduce the effectiveness of even the best hyperpigmentation treatment protocols.
Clinical Evaluation and Diagnosis of Pigmentation Disorders
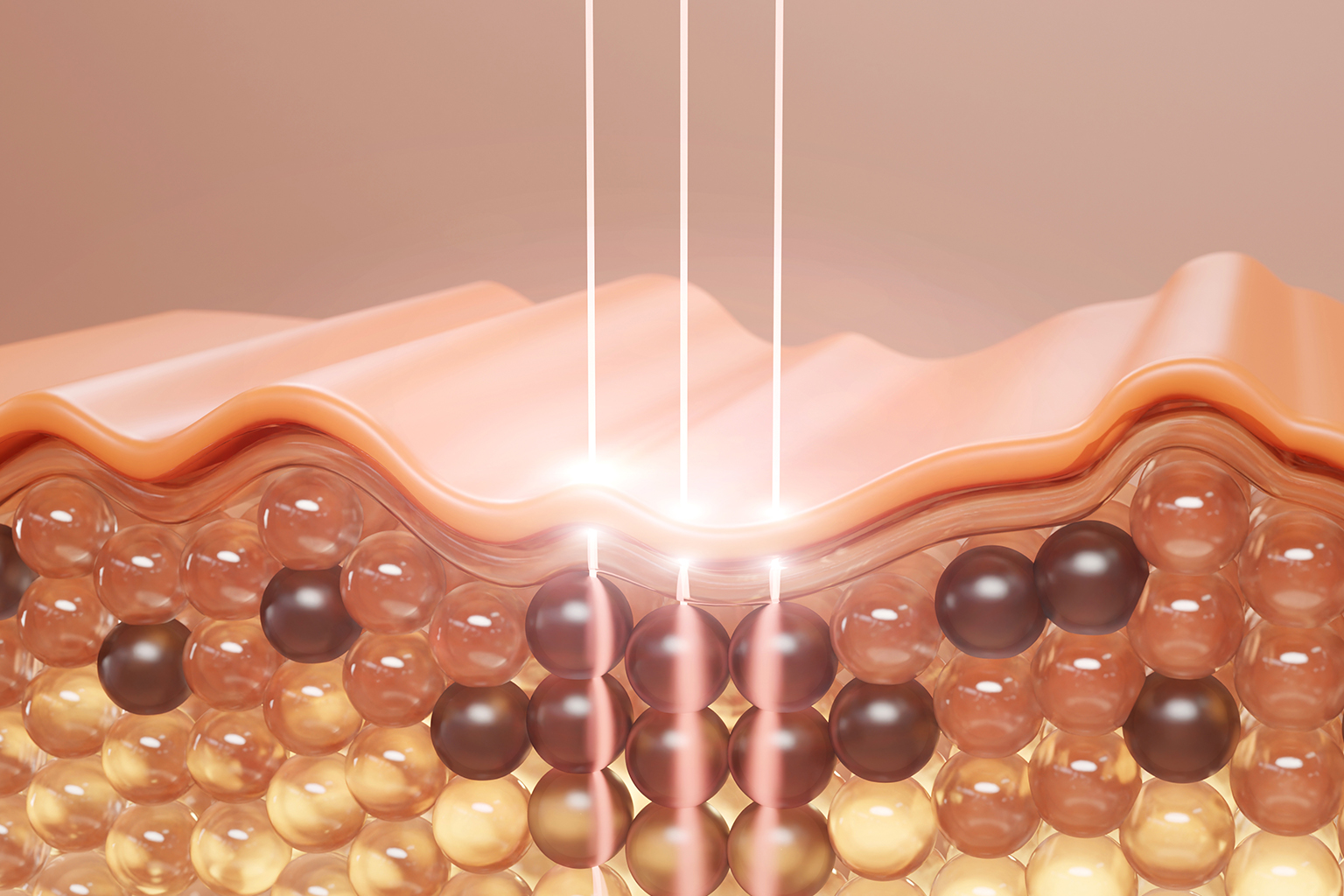
Effective management begins with defining what is pigmentation in skin for the individual patient. Clinical evaluation includes medical history, medication review, lifestyle factors, and Fitzpatrick skin type classification. These parameters influence treatment selection, expected response, and complication risk. From a diagnostic standpoint, what is pigmentation in skin varies significantly across pigmentary disorders.
Differentiating melasma, solar lentigines, and post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation is critical. Advanced diagnostic tools support precision-based care rather than generalized protocols. Establishing what is pigmentation in skin correctly ensures procedural options such as mesotherapy are selected appropriately and safely.
Hyperpigmentation Treatment Options: An Evidence-Based Overview
Available hyperpigmentation treatment options range from topical agents to in-clinic procedures. First-line management often includes azelaic acid, kojic acid, retinoids, and depigmenting combinations that suppress melanocyte activity and enhance epidermal turnover. For superficial cases, this form of hyperpigmentation treatment may be sufficient with prolonged, consistent use.
Procedural interventions such as chemical peels and laser therapies address deeper pigment but require clinical expertise, particularly in darker skin tones. Risk of rebound pigmentation has shifted focus toward safer, controlled approaches. This has led clinicians to evaluate modalities considered best for hyperpigmentation, balancing efficacy with skin barrier preservation and long-term safety.
Mesotherapy Whitening: A Targeted Clinical Approach

Mechanism of Action and Therapeutic Rationale
Mesotherapy whitening involves intradermal delivery of antioxidants, amino acids, vitamins, and depigmenting agents. Instead of relying on topical penetration, active compounds are placed directly within the melanocyte environment. This targeted delivery addresses tyrosinase inhibition, oxidative damage, and cellular repair simultaneously. Clinically, this method is regarded as best for hyperpigmentation when controlled pigment modulation is required.
At Serena Medical Center, formulations are customized based on pigmentation depth, distribution, and skin response. This individualized protocol supports gradual, medically supervised improvement. When evaluated against safety and consistency, mesotherapy whitening is frequently categorized as the best hyperpigmentation treatment for patients.
Procedure Protocol and Clinical Safety
Mesotherapy whitening is performed using microinjection techniques under strict aseptic conditions. Treatments are conducted exclusively by trained medical professionals. Session frequency typically ranges from two to four weeks, depending on response. Mild erythema or transient sensitivity may occur, while significant adverse events remain rare under protocol adherence.
Clinical studies demonstrate reduced pigment concentration and improved skin luminosity following treatment cycles. Beyond pigment correction, mesotherapy improves hydration and dermal quality. This integrated benefit profile supports its classification as best for hyperpigmentation when comprehensive skin health is a priority within structured hyperpigmentation treatment plans.
Outcomes, Maintenance, and Long-Term Skin Health
Sustained results depend on consistent post-procedure care. Broad-spectrum sunscreen use, barrier-repair formulations, and scheduled evaluations are mandatory. Patients who understand what causes hyperpigmentation demonstrate higher adherence and improved long-term outcomes following the best hyperpigmentation treatment approaches.
At Serena Medical Center, maintenance protocols are embedded within treatment planning. Follow-ups ensure progress stabilization and prevent recurrence. Long-term success in hyperpigmentation treatment relies on continued clinical oversight rather than isolated procedures.
Conclusion
A clear understanding of what is hyperpigmentation, its biological basis, and contributing triggers supports informed treatment decisions. Pigmentary disorders require precise diagnosis and individualized management strategies. Standardized approaches do not address the complexity of these conditions. Among advanced modalities, mesotherapy whitening is supported by evidence and clinical outcomes as a controlled, minimally invasive option.
For patients seeking resolution, expert evaluation remains essential. Structured care models that address both surface pigmentation and underlying biological drivers provide the most reliable outcomes. When performed within a medical framework, mesotherapy whitening remains aligned with protocols considered best hyperpigmentation treatment standards and best for hyperpigmentation management.
FAQs
What exactly is hyperpigmentation, and is it a medical condition?
Hyperpigmentation, which is characterized by dermal overpigmentation, is a condition involving the deposition of melanin in excess amounts in the skin. The medical aspect is considered not to be dangerous, but it is often a reflection of underlying factors that need to be evaluated clinically.What are the factors that contribute to the worsening of hyperpigmentation and the passage of time?
Exposure to the sun without protection, inflammation that is not treated, hormonal changes, and the wrong skincare can all contribute to the intensification and prolongation of the appearance of pigmentation.How does pigmentation occur in skin, and what is the normal regulation of the process?
The process of skin pigmentation is determined by the rate of melanin production by the melanocytes and the distribution of the melanin to the adjacent cells. The process is controlled by the interaction of genetics, hormones, and the environment.Is mesotherapy skin whitening suitable for all skin types?
The application of mesotherapy whitening by accredited medical practitioners is usually acceptable for all skin types; the protocols are modified based on the skin tone, sensitivity, and the depth of pigmentation.What is the top hyperpigmentation treatment that guarantees long-lasting results?
The top hyperpigmentation treatment includes the combination of a precise diagnosis, the application of clinical procedures such as mesotherapy whitening, and the use of medical-grade sun protection that is consistent for the long term results.
